The lab stages of the human menstrual cycle, a complex physiological process, play a pivotal role in fertility, contraception, and menstrual health. This comprehensive guide delves into the four distinct lab stages, their hormonal fluctuations, and their clinical significance.
Understanding the lab stages empowers individuals to optimize their reproductive health, plan for pregnancy, and detect menstrual disorders. This article provides an in-depth exploration of the lab stages, their monitoring methods, and their impact on overall well-being.
Lab Stages of the Human Menstrual Cycle
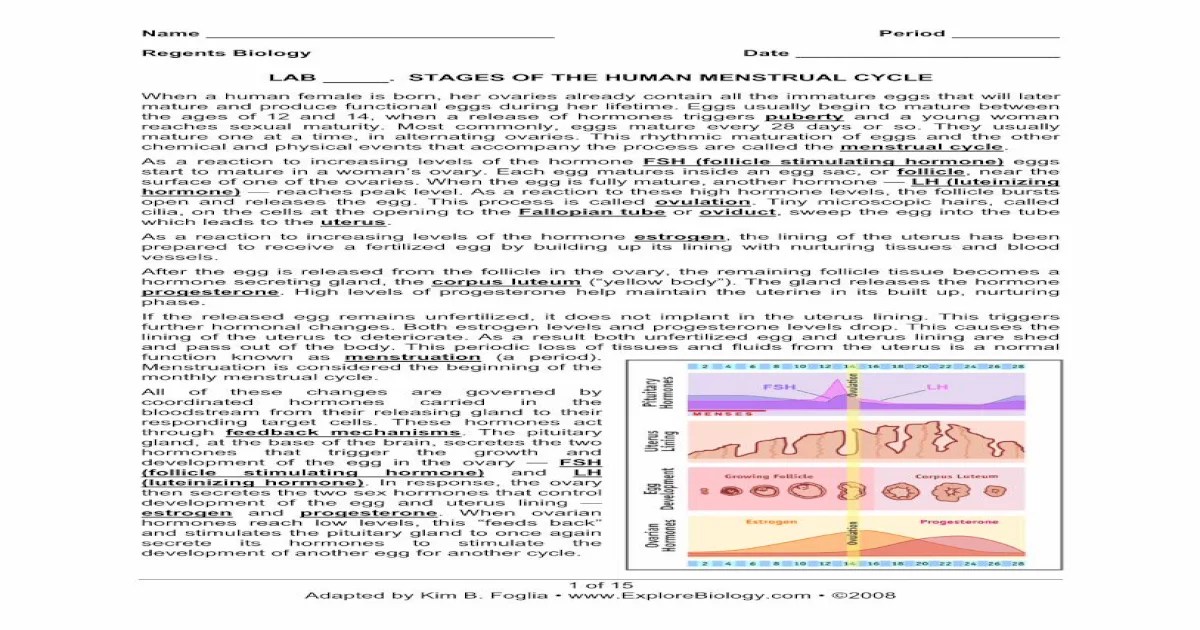
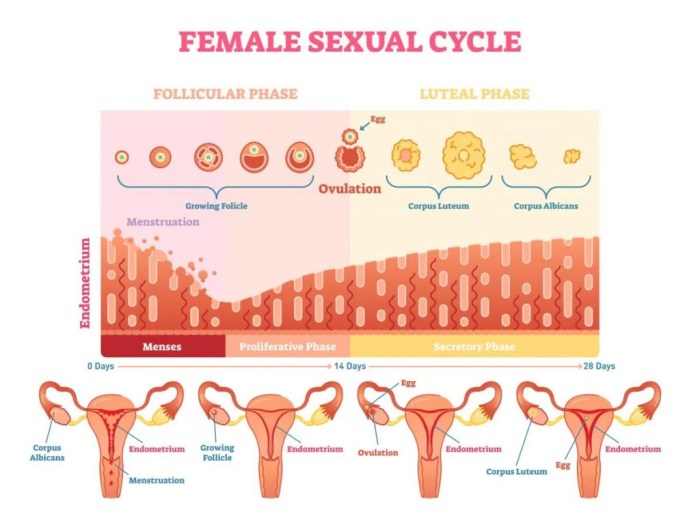
The human menstrual cycle consists of four distinct lab stages: menstrual, proliferative, ovulatory, and secretory. These stages are characterized by specific hormonal changes and physiological events.
The menstrual stage begins with the shedding of the uterine lining, known as menstruation. This stage is marked by a decrease in estrogen and progesterone levels.
The proliferative stage follows menstruation and is characterized by the growth of the uterine lining under the influence of increasing estrogen levels.
The ovulatory stage occurs when a mature egg is released from one of the ovaries. This stage is triggered by a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH).
The secretory stage follows ovulation and is characterized by the development of the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone. Progesterone prepares the uterine lining for implantation of a fertilized egg.
| Stage | Hormonal Changes | Physiological Events |
|---|---|---|
| Menstrual | Decrease in estrogen and progesterone | Shedding of uterine lining (menstruation) |
| Proliferative | Increase in estrogen | Growth of uterine lining |
| Ovulatory | Surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) | Release of egg from ovary (ovulation) |
| Secretory | Increase in progesterone | Development of corpus luteum |
Methods for Monitoring Lab Stages: Lab Stages Of The Human Menstrual Cycle
Various methods can be used to monitor the lab stages of the menstrual cycle:
- Basal body temperature charting:Measuring and recording body temperature upon waking to detect the temperature shift that occurs after ovulation.
- Ovulation predictor kits:Using urine tests to detect the surge in LH that triggers ovulation.
- Cervical mucus observation:Examining the consistency and amount of cervical mucus to identify changes that indicate ovulation.
Steps for Basal Body Temperature Charting:
- Take your temperature upon waking, before any activity.
- Record your temperature on a chart.
- Identify the temperature shift that occurs after ovulation.
Clinical Significance of Lab Stages
Understanding the lab stages of the menstrual cycle has clinical significance in:
- Fertility planning:Identifying the fertile window and timing intercourse accordingly.
- Contraception:Using methods that target specific lab stages, such as hormonal contraception or the rhythm method.
- Diagnosis of menstrual disorders:Identifying abnormalities in the lab stages can help diagnose conditions such as amenorrhea, oligomenorrhea, and polycystic ovary syndrome.
Flowchart for Fertility Planning Using Lab Stages:
- Start monitoring your menstrual cycle using basal body temperature charting or ovulation predictor kits.
- Identify the fertile window (5 days before ovulation and the day of ovulation).
- Time intercourse during the fertile window to increase the chances of conception.
Impact of Lifestyle Factors on Lab Stages
Lifestyle factors can influence the lab stages of the menstrual cycle:
- Stress:Chronic stress can disrupt hormone production and affect ovulation.
- Exercise:Intense exercise can suppress ovulation in some women.
- Nutrition:Extreme weight loss or gain can alter hormone levels and affect menstrual regularity.
| Lifestyle Factor | Effects on Lab Stages |
|---|---|
| Stress | Disruption of hormone production, impaired ovulation |
| Exercise | Suppression of ovulation (in some women) |
| Nutrition | Alteration of hormone levels, irregular menstrual cycles |
Recent Advancements in Lab Stage Monitoring
Technological advancements have improved lab stage monitoring:
- Wearable devices:Track body temperature, heart rate, and other physiological parameters to identify ovulation.
- Smartphone apps:Provide personalized cycle tracking, fertility predictions, and access to expert advice.
- Hormone monitoring:Blood or saliva tests can measure hormone levels and provide insights into lab stages.
Potential Future Directions for Research:
- Developing more accurate and accessible methods for lab stage monitoring.
- Investigating the impact of environmental factors on menstrual cycles.
- Exploring the role of lab stages in reproductive health and disease.
Clarifying Questions
What are the four lab stages of the menstrual cycle?
The four lab stages are the menstrual, proliferative, ovulatory, and secretory stages.
How can I monitor my lab stages?
Methods for monitoring lab stages include basal body temperature charting, ovulation predictor kits, and cervical mucus observation.
What is the clinical significance of understanding the lab stages?
Understanding the lab stages is crucial for fertility planning, contraception, and diagnosing menstrual disorders.