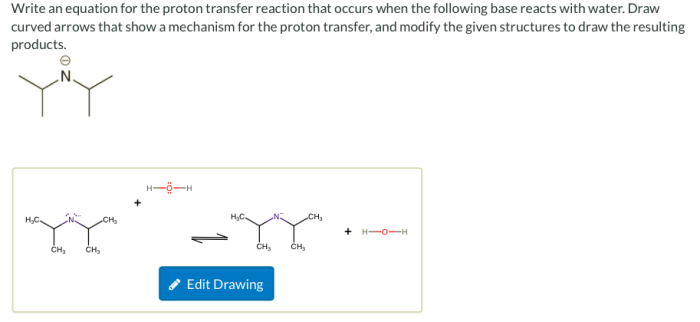
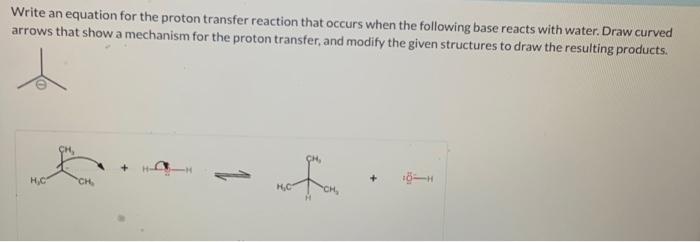
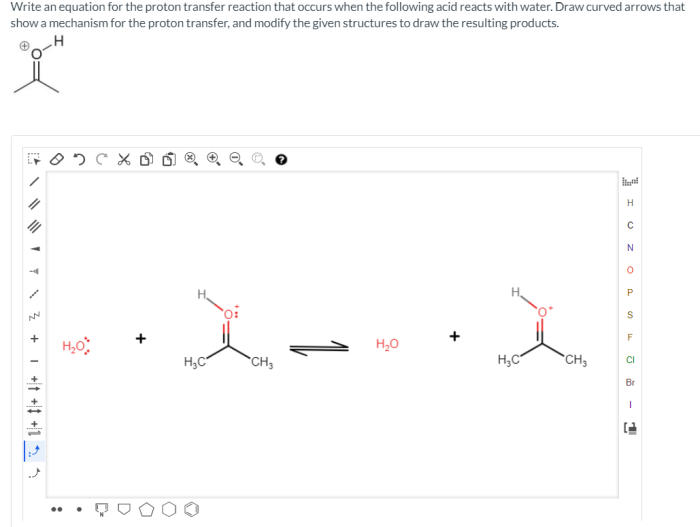
Write an equation for the proton transfer reaction that occurs, a fundamental process in chemistry and biology. This equation encapsulates the transfer of a proton (H+) from one species to another, leading to the formation of new chemical species. Understanding this equation is crucial for comprehending various chemical reactions and their applications.
Proton transfer reactions play a vital role in numerous fields, including acid-base chemistry, enzyme catalysis, and biological processes. By delving into the equation for proton transfer reactions, we gain insights into the behavior of protons in aqueous solutions, the role of acids and bases, and the pH concept.
Proton Transfer Reaction Equation
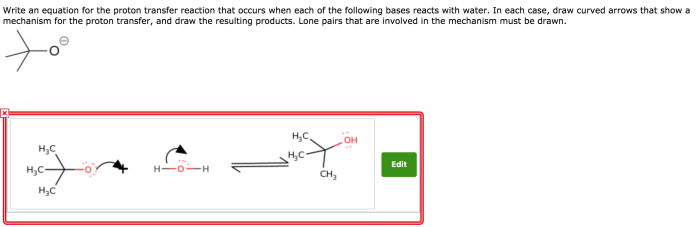
A proton transfer reaction is a chemical reaction in which a proton (H +ion) is transferred from one molecule or ion to another.
The general equation for a proton transfer reaction can be written as:
HA + B → A–+ HB +
where HA is the acid, B is the base, A –is the conjugate base of the acid, and HB +is the conjugate acid of the base.
Acid-Base Reactions
Acids are substances that donate protons, while bases are substances that accept protons.
The Bronsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases states that an acid is a substance that can donate a proton, and a base is a substance that can accept a proton.
Some examples of acid-base reactions involving proton transfer include:
- HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H 2O
- CH 3COOH + NH 3→ CH 3COONH 4
- H 2SO 4+ 2NaOH → Na 2SO 4+ 2H 2O
Proton Transfer in Aqueous Solutions, Write an equation for the proton transfer reaction that occurs
In aqueous solutions, protons are hydrated and exist as H 3O +ions.
The pH of a solution is a measure of its acidity or alkalinity, and is defined as the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration.
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation can be used to calculate the pH of a solution:
pH = pKa+ log([A –]/[HA])
where pK ais the acid dissociation constant of the acid.
Applications of Proton Transfer Reactions
Proton transfer reactions are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Chemistry: Proton transfer reactions are used in the synthesis of many organic and inorganic compounds.
- Biology: Proton transfer reactions are involved in many biological processes, such as enzyme catalysis and ATP synthesis.
- Medicine: Proton transfer reactions are used in the development of drugs and other medical treatments.
- Environmental science: Proton transfer reactions are involved in the formation of acid rain and other environmental processes.
FAQ Compilation: Write An Equation For The Proton Transfer Reaction That Occurs
What is the general form of the proton transfer reaction equation?
The general equation for a proton transfer reaction is: HA + B → A- + HB+, where HA is the acid, B is the base, A- is the conjugate base of HA, and HB+ is the conjugate acid of B.
How does the Bronsted-Lowry theory define acids and bases?
According to the Bronsted-Lowry theory, an acid is a substance that can donate a proton, while a base is a substance that can accept a proton.
What is the relationship between pH and proton concentration?
pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution and is inversely related to proton concentration. A lower pH indicates a higher proton concentration, while a higher pH indicates a lower proton concentration.