Which of the following is true of a radiopaque substance? This question delves into the realm of medical imaging, where the use of radiopaque substances plays a crucial role in enhancing the visibility of anatomical structures during diagnostic procedures. Understanding the properties and applications of radiopaque substances is essential for medical professionals and individuals seeking a deeper understanding of medical imaging techniques.
Radiopaque substances, also known as contrast agents, are materials that absorb or scatter X-rays, making them appear opaque on medical images. Their unique ability to interact with radiation allows them to highlight specific organs, tissues, or blood vessels, providing valuable insights into their structure and function.
1. Introduction
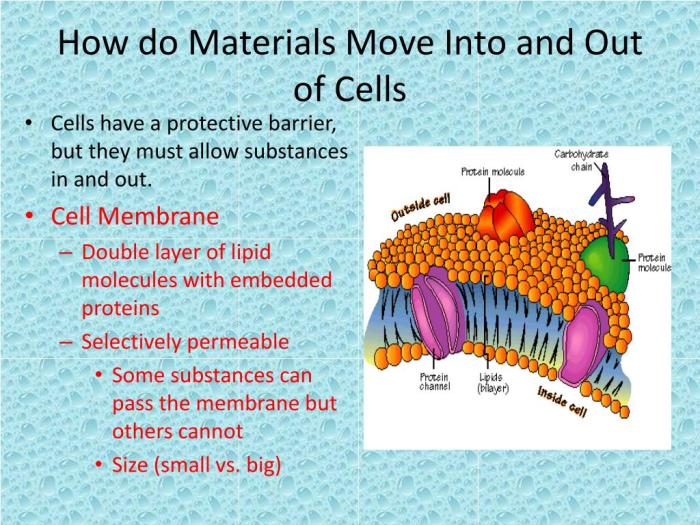
A radiopaque substance is a material that does not allow X-rays to pass through it, making it appear opaque on an X-ray image. Radiopaque substances are essential in medical imaging as they enhance the visibility of specific structures or organs, allowing for more accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
2. Types of Radiopaque Substances
| Type | Composition | Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Barium sulfate | Barium sulfate (BaSO4) | High density, insoluble in water, commonly used in gastrointestinal imaging |
| Iodine-based contrast agents | Iodine bound to organic molecules | Water-soluble, used in vascular imaging, CT scans, and MRI |
| Gadolinium-based contrast agents | Gadolinium chelates | Water-soluble, used in MRI to enhance the visibility of blood vessels and organs |
| Air | Nitrogen and oxygen gases | Low density, used as a contrast agent in certain imaging procedures, such as double-contrast barium enemas |
3. Mechanisms of Action
Radiopaque substances interact with X-rays by absorbing or scattering them. This interaction is known as attenuation. The density and atomic number of the radiopaque substance determine the degree of attenuation. Higher density and atomic number substances attenuate X-rays more effectively, resulting in greater opacity on X-ray images.
4. Applications in Medical Imaging: Which Of The Following Is True Of A Radiopaque Substance
- Barium enemas:Used to visualize the colon and rectum.
- Upper gastrointestinal series:Used to visualize the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum.
- Angiography:Used to visualize blood vessels.
- CT scans:Used to visualize cross-sectional images of the body.
- MRI:Used to visualize soft tissues and organs.
5. Safety and Considerations
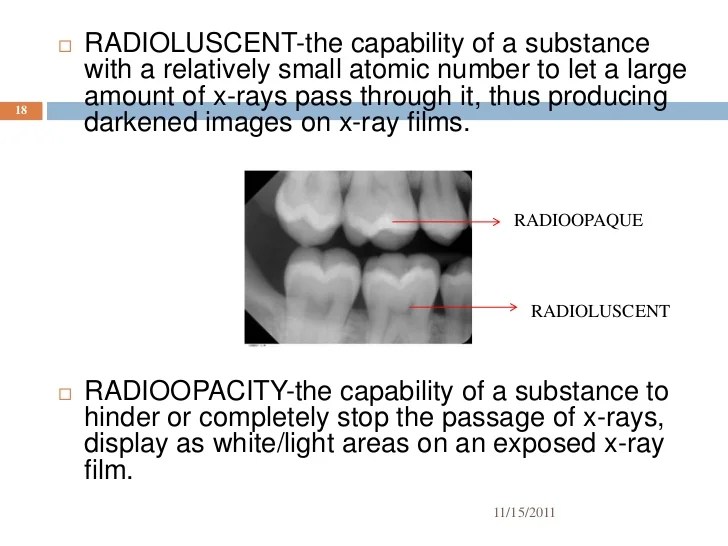
Radiopaque substances can have potential risks and side effects, including allergic reactions, nausea, vomiting, and kidney damage. The choice of radiopaque substance depends on the specific imaging procedure and the patient’s health condition. Precautions are taken to minimize risks, such as administering pre-medications to prevent allergic reactions and monitoring kidney function before and after the procedure.
FAQ Resource
What is the primary function of a radiopaque substance?
Radiopaque substances enhance the visibility of anatomical structures during medical imaging by absorbing or scattering X-rays.
How do radiopaque substances interact with X-rays?
Radiopaque substances contain elements with high atomic numbers, which effectively absorb or scatter X-rays, resulting in their appearance as opaque areas on medical images.
What are some common types of radiopaque substances?
Iodine-based contrast agents, barium sulfate, and gadolinium-based contrast agents are commonly used radiopaque substances.
What are the potential risks associated with radiopaque substances?
Radiopaque substances can cause allergic reactions, kidney damage, and other side effects in some individuals. However, these risks are generally low and can be minimized with proper precautions.