Embark on an enlightening journey into the realm of motor neurons, the unsung heroes that orchestrate our every physical movement. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the intricate mechanisms of neuron that allows for physical movement crossword, unriddle the complexities of muscle contraction, and uncover the profound medical implications of motor neuron disorders.
As we navigate through this intricate tapestry of biological processes, we will unravel the secrets of how our brains communicate with our muscles, triggering the symphony of motion that defines our physical existence.
Motor Neurons
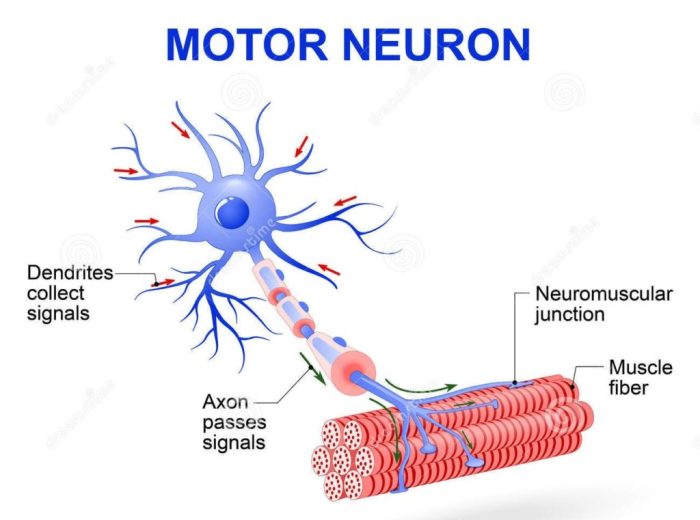
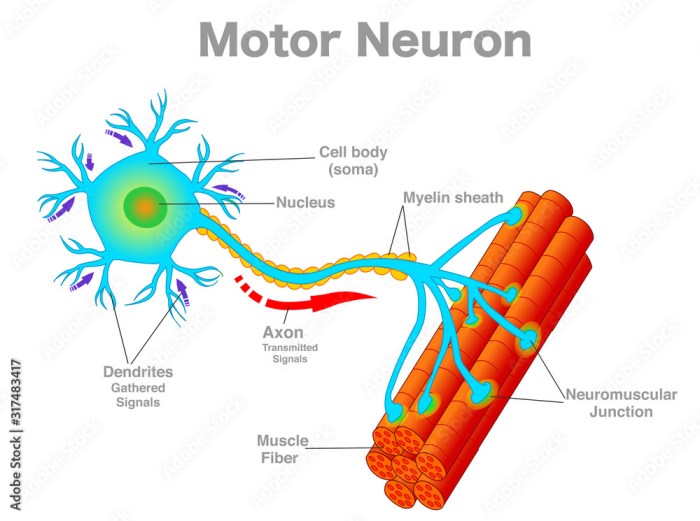
Motor neurons are nerve cells that transmit signals from the brain and spinal cord to muscles, enabling physical movement. They play a crucial role in controlling voluntary and involuntary muscle actions.
Motor neurons receive signals from the central nervous system and send them to muscles through axons, long, slender extensions of the neuron. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal, it triggers the release of neurotransmitters, chemical messengers that bind to receptors on the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.
Types of Motor Neurons, Neuron that allows for physical movement crossword
- Alpha motor neurons:Innervate extrafusal muscle fibers, which are responsible for generating force and movement.
- Gamma motor neurons:Innervate intrafusal muscle fibers, which help regulate muscle tone and length.
- Fusimotor neurons:Innervate muscle spindles, sensory receptors that provide feedback on muscle length and contraction.
Crossword Puzzle
Clue:Neuron that allows for physical movement
| M | O | T | O | R | N | E | U | R |
| O | N | N |
Muscle Contraction
Muscle contraction is the process by which muscles shorten and generate force. It is initiated by motor neurons triggering the release of calcium ions into the muscle fiber.
Calcium ions bind to receptors on the sarcoplasmic reticulum, an internal membrane system within the muscle fiber. This causes the release of more calcium ions, leading to a cascade of events that result in the sliding of actin and myosin filaments past each other, causing muscle shortening.
Neuromuscular Junction
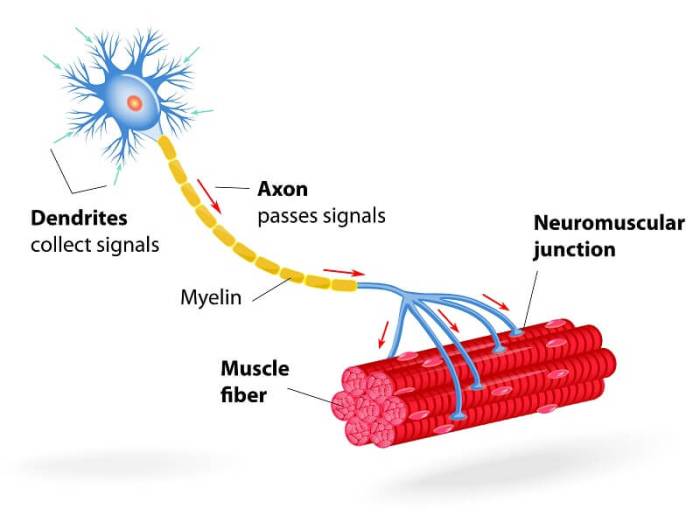
The neuromuscular junction is the specialized synapse where motor neurons communicate with muscle fibers. It consists of the axon terminal of the motor neuron and the motor end plate on the muscle fiber.
When an action potential reaches the axon terminal, it triggers the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter. Acetylcholine binds to receptors on the motor end plate, causing the opening of ion channels and the generation of an action potential in the muscle fiber, leading to muscle contraction.
Medical Implications
Motor neuron disorders are a group of conditions that affect motor neurons, leading to muscle weakness, atrophy, and paralysis. These disorders can be inherited or acquired and range in severity from mild to fatal.
Examples of motor neuron disorders include amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), spinal muscular atrophy, and progressive supranuclear palsy. Treatments for motor neuron disorders focus on managing symptoms and improving quality of life, as there is currently no cure.
FAQs: Neuron That Allows For Physical Movement Crossword
What is the role of motor neurons in physical movement?
Motor neurons are the messengers that transmit signals from the brain to muscles, initiating and controlling all voluntary movements.
How does muscle contraction occur?
Muscle contraction is triggered by motor neurons releasing calcium ions, which bind to proteins within muscle fibers, causing them to slide past each other and shorten.
What is the neuromuscular junction?
The neuromuscular junction is the specialized synapse where motor neurons communicate with muscle fibers, releasing neurotransmitters that trigger muscle contraction.
What are the medical implications of motor neuron disorders?
Motor neuron disorders disrupt the communication between the brain and muscles, leading to muscle weakness, paralysis, and other debilitating symptoms.
What are the treatments for motor neuron disorders?
Treatments for motor neuron disorders focus on managing symptoms, slowing disease progression, and improving quality of life, including medications, physical therapy, and assistive devices.
