Discover the fascinating diversity of North America’s biomes in this comprehensive guide, “Biomes of North America PDF.” Embark on a journey through the continent’s unique ecosystems, from sprawling grasslands to towering coniferous forests and pristine aquatic environments.
This meticulously crafted guide unveils the intricate tapestry of life that characterizes each biome, exploring their distinct climates, vegetation, and wildlife. Prepare to be captivated by the ecological wonders that shape the face of North America.
North American Biome Overview
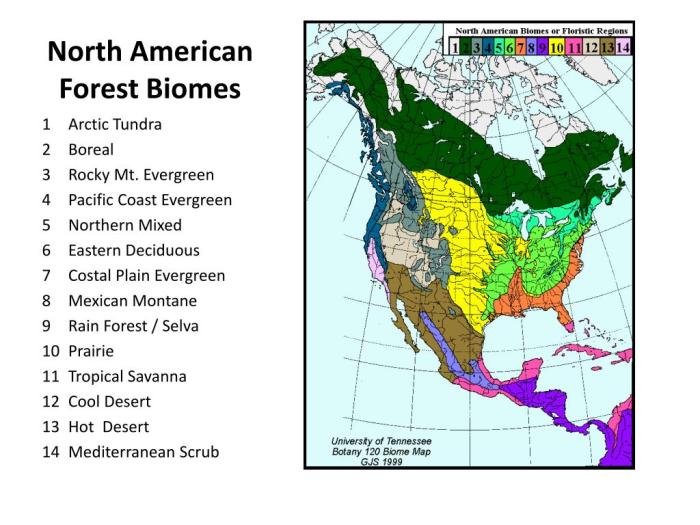
Biomes are large, distinct ecological communities characterized by specific climates, vegetation, and animal life. They are determined by a combination of factors including latitude, elevation, precipitation, and soil type. North America is home to a diverse range of biomes, each with its own unique set of characteristics.
Major Biomes of North America
The major biomes of North America include:
-
-*Tundra
Cold, treeless regions with low precipitation and permafrost.
-*Boreal Forest
Coniferous forests found in northern latitudes with cold, snowy winters and short, warm summers.
-*Temperate Forest
Deciduous and mixed forests found in mid-latitudes with moderate temperatures and precipitation.
-*Grassland
Open, treeless regions with moderate precipitation and a mix of grasses and wildflowers.
-*Desert
Arid regions with little precipitation and sparse vegetation.
-*Chaparral
Shrublands found in Mediterranean climates with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters.
-*Temperate Rainforest
Forests found in coastal regions with high precipitation and mild temperatures year-round.
Temperate Deciduous Forest Biome
Temperate deciduous forests are characterized by their broad-leaved trees that lose their leaves seasonally, typically during autumn. These forests are found in temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere, including eastern North America, Europe, and parts of Asia.
Climate
Temperate deciduous forests experience warm, humid summers and cool, moist winters. Precipitation is typically evenly distributed throughout the year, with slightly more rain during the summer months. The average annual temperature ranges from 50°F (10°C) to 60°F (16°C).
Vegetation, Biomes of north america pdf
The dominant trees in temperate deciduous forests are oaks, maples, birches, beeches, and hickories. These trees have broad leaves that allow them to photosynthesize efficiently during the growing season. The understory vegetation is typically composed of shrubs, wildflowers, and ferns.
Wildlife
Temperate deciduous forests are home to a wide variety of wildlife, including deer, squirrels, raccoons, foxes, and birds. These animals rely on the trees for food, shelter, and nesting sites. The forests also provide important habitat for migratory birds during the spring and fall.
Ecological Importance
Temperate deciduous forests play a vital role in the global ecosystem. They help to regulate the climate by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen. They also provide important habitat for wildlife, protect watersheds, and offer recreational opportunities.
Grassland Biome: Biomes Of North America Pdf
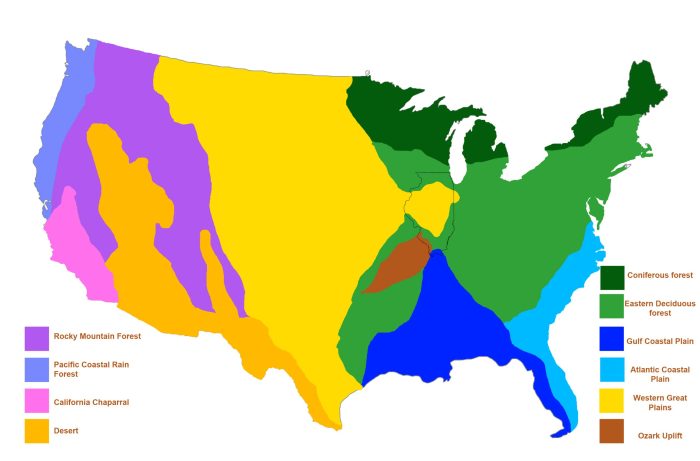
The grassland biome, also known as the temperate grassland or prairie, is characterized by its vast, treeless expanses dominated by grasses and other herbaceous plants. These grasslands are found in regions with moderate rainfall and seasonal temperature variations.
Grasslands are vital ecosystems that support a diverse array of plant and animal life. They play a crucial role in the global carbon cycle, storing vast amounts of carbon in their deep root systems. Additionally, grasslands provide essential grazing lands for livestock and support numerous species of birds, mammals, and insects.
Climate
Grasslands experience a continental climate with warm summers and cold winters. Precipitation is moderate, ranging from 25 to 75 centimeters annually. The distribution of rainfall is often seasonal, with most precipitation occurring in the spring and summer months.
Vegetation, Biomes of north america pdf
The vegetation of grasslands is primarily composed of grasses and other herbaceous plants. Dominant grass species include buffalo grass, blue grama, and western wheatgrass. Other common plants include wildflowers, sedges, and rushes.
Wildlife
Grasslands support a diverse array of wildlife. Large herbivores such as bison, pronghorn, and elk graze on the grasses, while smaller mammals like prairie dogs, ground squirrels, and rabbits inhabit the burrows and tunnels they create in the soil.
Grasslands are also home to a variety of birds, including meadowlarks, sparrows, and hawks. Raptors such as eagles and falcons hunt over the open grasslands, while owls roost in trees and hunt at night.
Desert Biome
Deserts are arid regions that receive less than 25 centimeters of precipitation annually. They are characterized by extreme temperatures, sparse vegetation, and unique wildlife adaptations. Deserts cover about one-third of the Earth’s land surface and are found on all continents except Antarctica.
The climate of deserts is characterized by high temperatures and low humidity. During the day, temperatures can soar to over 50 degrees Celsius (122 degrees Fahrenheit), while at night, they can drop to below freezing. The lack of humidity means that deserts experience very little rainfall.
In some deserts, it may not rain for years at a time.
Vegetation, Biomes of north america pdf
The vegetation of deserts is adapted to the harsh conditions. Plants have deep roots to reach water deep in the ground. They also have thick, waxy leaves to reduce water loss through evaporation. Some desert plants, such as cacti, have spines to protect themselves from animals.
Wildlife
The wildlife of deserts is also adapted to the harsh conditions. Animals are active at night when temperatures are cooler. They have long legs to help them move quickly across the sand. Some desert animals, such as camels, have humps that store fat to help them survive during long periods without food.
Ecological Importance
Deserts play an important ecological role. They are home to a variety of unique plants and animals. Deserts also help to regulate the Earth’s climate by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen.
Get the inside scoop on the diverse biomes of North America with our comprehensive PDF guide. For those seeking a mathematical challenge, check out our Abeka Algebra 2 Quiz 34 . Afterward, return to the fascinating world of North American biomes and explore their unique characteristics, from lush forests to arid deserts.
Tundra Biome
The tundra biome is a vast, treeless expanse found in the Arctic and subarctic regions of North America. This cold, harsh environment is characterized by permafrost, a layer of soil that remains frozen throughout the year. The tundra is home to a unique assemblage of plants and animals that have adapted to the extreme conditions.
Climate
The tundra biome is characterized by a cold, dry climate. Temperatures can drop below -40 degrees Fahrenheit in the winter, and the average annual temperature is below freezing. The tundra receives very little precipitation, with most of it falling as snow.
The long, cold winters and short, cool summers make the tundra a challenging environment for life.
Vegetation, Biomes of north america pdf
The vegetation of the tundra is low-growing and sparse. The most common plants are lichens, mosses, and sedges. These plants are able to survive in the harsh conditions of the tundra because they have adapted to the cold, dry climate and the nutrient-poor soil.
Trees are absent from the tundra, except for a few stunted willows and alders that grow in the southernmost regions.
Wildlife
The tundra is home to a variety of animals that have adapted to the cold, harsh environment. These animals include caribou, reindeer, musk oxen, wolves, and polar bears. The tundra also provides a breeding ground for many migratory birds, such as snow geese and sandhill cranes.
Ecological Importance
The tundra biome plays an important role in the global ecosystem. The tundra is a carbon sink, meaning that it absorbs more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere than it releases. The tundra also helps to regulate the global climate by reflecting sunlight back into space.
Coniferous Forest Biome
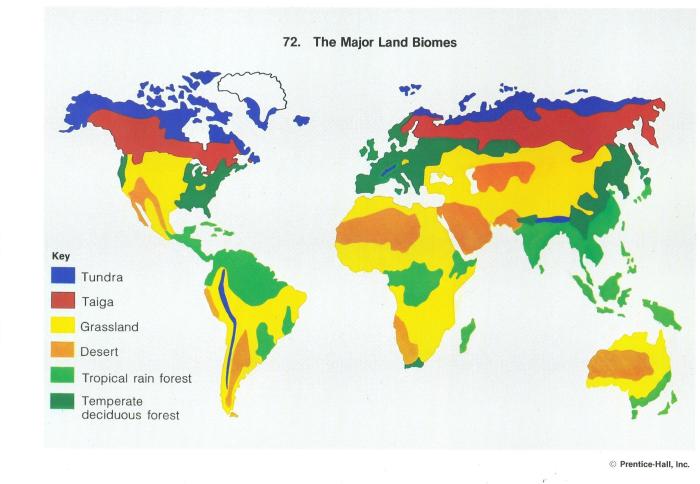
Coniferous forests, also known as taigas, are vast ecosystems characterized by their dense populations of coniferous trees, such as pines, firs, and spruces. These forests play a crucial role in the Earth’s ecosystem, providing habitats for diverse wildlife and regulating the global climate.
Climate
Coniferous forests experience long, cold winters with heavy snowfall and short, mild summers. The average annual temperature ranges from -5°C to 10°C, with annual precipitation between 50 and 150 centimeters.
Vegetation, Biomes of north america pdf
Coniferous trees are the dominant vegetation in this biome, forming dense stands that block out much of the sunlight. These trees have needle-like leaves that are coated in a waxy substance to prevent water loss during the cold winters. Other common plants in coniferous forests include shrubs, mosses, and ferns.
Wildlife
Coniferous forests are home to a diverse array of wildlife, including large mammals such as moose, bears, and wolves. Other common animals include squirrels, rabbits, and a variety of bird species. The cold climate and dense vegetation provide shelter and food for these animals.
Ecological Importance
Coniferous forests play a vital role in the Earth’s ecosystem. They are important carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and releasing oxygen. They also help regulate the water cycle, absorbing and releasing water slowly, which prevents flooding and droughts.
Aquatic Biomes
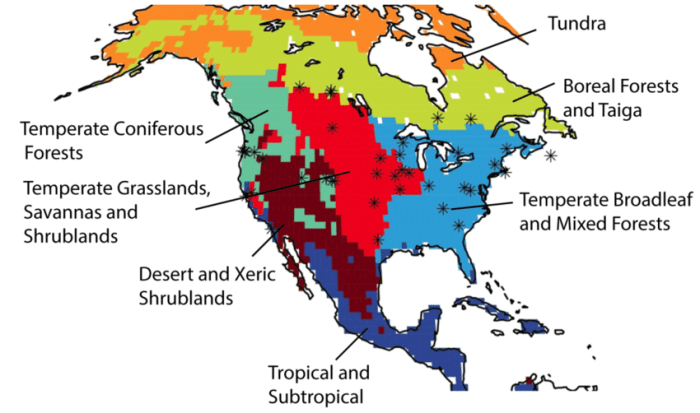
Aquatic biomes in North America encompass a diverse range of ecosystems, from freshwater lakes and rivers to coastal estuaries and oceans. These biomes support a vast array of aquatic life, including fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals.
Climate
The climate of aquatic biomes varies depending on their location and altitude. Freshwater biomes typically experience temperate climates with warm summers and cold winters, while coastal biomes are influenced by the moderating effects of the ocean, resulting in milder temperatures year-round.
Vegetation, Biomes of north america pdf
Vegetation in aquatic biomes is primarily composed of aquatic plants, such as algae, water lilies, and cattails. These plants provide food and shelter for a variety of aquatic organisms.
Wildlife
Aquatic biomes are home to a diverse array of wildlife, including fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. Fish are the most abundant vertebrates in aquatic biomes, and they play a vital role in the food chain. Amphibians, such as frogs and salamanders, are also common in aquatic biomes, and they often rely on aquatic habitats for breeding and feeding.
Ecological Importance
Aquatic biomes provide a number of important ecological services, including water filtration, flood control, and nutrient cycling. They also provide habitat for a variety of plants and animals, and they support recreational activities such as fishing, boating, and swimming.
FAQ Resource
What are the major biomes of North America?
The major biomes of North America include temperate deciduous forests, grasslands, deserts, tundra, coniferous forests, and aquatic biomes.
How do biomes influence the distribution of plant and animal life?
Biomes provide specific environmental conditions that determine the types of plants and animals that can thrive within them. Factors such as climate, soil, and water availability shape the ecological communities found in each biome.
Why are biomes important for conservation?
Biomes represent distinct and irreplaceable ecosystems that support a wide range of species and ecological processes. Conserving biomes is crucial for maintaining biodiversity, ecosystem services, and the overall health of the planet.